English Magpie Pigeon: Behavior and More
Long live the queen! I’m not talking about the Former Queen Elizabeth but the queen of pigeons in England. That’s right, it’s none other than English Magpie Pigeon.
Elongated black and white tails, yellow beak and well-proportioned body structure make it eye-catching. Its social nature makes it perfect for pets.
Just like a royal, it’s fancy and needs high maintenance. Check out the origin, traits and nature of the English Magpie Pigeon Below.
English Magpie Pigeon Profile
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Columba Livia Domestica |
| Common Names | Magpie Pigeon, White Magpie Pigeon |
| Origin | 19th century, England |
| Size | 12 to 14 inches in length. |
| Weight | 10 to 14 ounces |
| Lifespan | 5 to 10 years |
| Physical Features | Black and white plumage, Fan-shaped tail, Sleek body, Medium-sized, |
| Temperament | Clam and human-friendly |
| Behavior | Social and strong pair bonds |
| Special Features | Homing instinct, pigeon racing, pigeon pageants |
| Breeding and Maintenance | Selective breeding, balanced diet, predator protection |
| Common or Popular Varieties | Black and white plumage, teal or blue plumage, yellow beak |
Interested in similar topics on pigeon breed:
Overview Of English Magpie Pigeon
The English Magpie Pigeon, or Columba livia domestica, is a pigeon breed known for its appearance. It has black and white plumage and a striking fan-shaped tail.

This pigeon’s history goes way back to the 1900s and was bred for appearance. Sometimes, it was used as a messenger due to its homing instinct.
Besides black and white plumage, teal or blue plumage, Magpie Pigeons can be found in England.
History And Origins of English Magpie Pigeons
English Magpie Pigeons are also known as “Queen of Pigeons” in Britain. The history and origin of these fancy pigeons go back to the Victorian era.
In the 19th century, breeding pigeons was a popular pastime among the nobles. Magpies are the descendants of Rock Pigeons. Some argue that English Magpies came from Tumbler breeds and that too from Denmark.

So, these pigeons have gone through many crosses. Baghdad pigeon crosses have created the current English Magpie, which all adore. These pigeons have gone through selective breeding, no surprise.
Breeders wanted to create a beautiful pigeon with black and white patterns or markings. They also wanted English Magpies to resemble the Eurasian ones. Moreover, the focus was on the plumage and desired traits.
Physical Characteristics And Features
English Magpies are medium-sized and have fan tail feathers. Their looks make them beloved among pigeon fanciers.

At a glance –
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Size | Medium to large-sized birds, measuring 17-21 inches in length |
| Weight | 1.3-1.9 lbs |
| Legs | Two dark feet with three thin toes pointing forward and one pointing backward |
| Heads | Small, dark eyes |
| Bills | Long and flesh-colored |
| Eyes | Small, dark eyes |
| Colors | Striking black and white plumage, long tails, and raucous calls |
| Personality Traits | Intelligent, easily tamed, monogamous, and long-lived |
| Purposes | Omnivores, tool-using, and vocal mimics |
| Incubation Period | 16-19 days |
| Lifespan | Up to 15 years in the wild |
Appearance
How can you detect an English Magpie? Check the pigeon body for any white and black plumage. It’s a classic marking of any magpie.
The head, neck, back and tail are black and the rest of the body is white. Also, it gives a metallic appearance.
They are medium-sized and have a sleek body. Most of the English Magpies have well-proportioned structures. Also, these pigeons have wingspan lengths from 49 to 51 cm.
In case of any exhibitions, black magpie pigeons are preferable. A combination of yellow-black and silver-black is also desirable among pigeon fanciers.
Size and Body Structure
English Magpie pigeons have 12 to 14 inches of body length. They have small heads, but they balance their physique with the help of their long and slender neck.
This is a unique physical feature of English Magpie pigeons. The strong body of these birds allows them to maintain balance even with a long and slender neck.
English Magpie Pigeons’ main body is white and the rest of the area is black or teal or different colors. The beak length is medium and they have a strong neck.
Unique Features
English Magpie pigeons have exquisite fan-shaped tails. Tail feathers resemble peacock feather patterns. The feathers are broad and fan out beautifully. However, the contrast of black and white makes them captivating.
Common Variation
The variations include increased black markings, some have unique patterns. Others may have green, teal feathers and yellow beaks. There are some rare patterns among this breed as well.
Distribution And Habitat of English Magpie Pigeons
These were bred through selective breeding, so English Magpies are popular as pets.

Geographic Distribution
These birds are domesticated and bred worldwide by pigeon fanciers. Naturally, these are found in Britain and some parts of the U.S.A.
However, New York and New Jersey have an exclusive collection of English Magpie Pigeons due to the bird’s appearance.
Habitat Preferences
The English Magpie pigeons come from selective breeding and are generally domesticated, meaning they usually live in captivity. These birds prefer being taken care of by human caregivers.
Similar to any other pigeons, they also look for comfort, safety and availability of food when searching for a habitat. Open spaces are a must for these birds as they like to take flight from time to time.
Urban and Rural Habitats
English Magpie Pigeons are strong and adaptable pigeons. So, they are comfortable in both rural and urban settings.
That being said, these are fancy pigeons and bred for their unique looks, so you will encounter them mostly in urban areas rather than in rural habitats.
In both rural and urban settings, these pigeons prefer secure and weatherproof spaces where there is an ample amount of food and water.
Migration and Seasonal Movements
As domesticated pigeons, they don’t show any migratory instinct. So, there are not any seasonal movements because they live in captivity. Often, caregivers provide every necessity when the season changes.
Threats and Conservation Status
English Magpie Pigeons are a well-preserved species. It is popular worldwide and so breeders always make sure of their well-being. But like any other bird, they do face threats from diseases, predators and extreme weather.
Behavior And Traits of English Magpie Pigeons
Magpie Pigeons are gentle and are great pets. However, they love a seed-based diet.
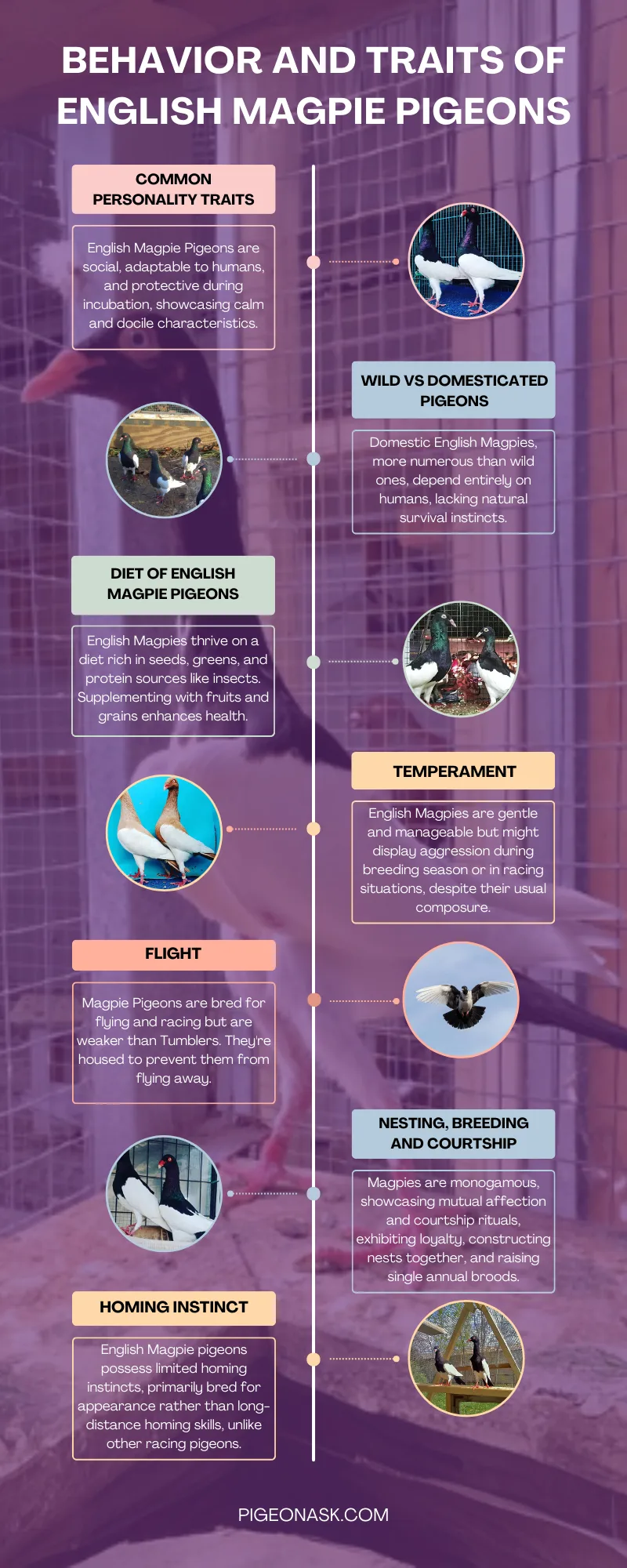
Common Personality Traits
These birds are docile and have calm characteristics. English Magpie Pigeons are social and chatty. They easily mix up with other breeds of pigeons or birds.
Moreover, these pigeons are adaptable to human presence but protective during incubation.
Differences Between Wild and Domesticated Pigeons
Wild English Magpies are lower in number in contrast to domesticated ones. Most pets have lost their survival and migratory instincts.
Wild ones are independent, but the domestic ones rely completely for everything on human caregivers.
Diet
These pigeons prefer a seed and green-based diet along with clean drinking water. It’s better to feed a diet with constant protein (mullet, insects) too. Spinach, sunflower seeds, fruits and sometimes a bit of popcorn keep them healthy.
Temperament
English Magpies are docile and easy to handle. They do not take part in races like tumblers. But some of them do. In the case of racing, they can get a bit aggressive.
While they will remain calm and composed throughout the year, during their breeding season, these birds show signs of aggressiveness.
Flight
Magpie Pigeons are bred for their exceptional flying skills. So they can fly and also race against other birds. But they are not as strong as Tumblers.
Generally, they are kept in a loft to prevent flying away from home. This is due to the fact that even though they have homing instincts, they can fly away as it’s a part of a bird’s nature.
Nesting, Breeding and Courtship
They are monogamous and hold strong pair bonds. Male pigeons coo and puff their plumage to woo their female counterparts. Nesting ones show affectionate behavior and mutual preening.
Courtship Ballet
Magpie courtship transforms into a visual spectacle, where the male dazzles with feather puffing, wing displays, and playful hops. This avian dance reaches its crescendo as the male offers tokens of affection in the form of food.
The enduring monogamous nature of magpie pairs paints a picture of consistency, forging a narrative of loyalty and enduring commitment.
Nesting Insights
Magpies, known for their architectural prowess, construct substantial nests blending twigs and sticks, crowned with a mud cup crafted collaboratively by both male and female.
Nesting spots vary, showcasing magpies’ adaptability, often forming loose colonies.
Breeding Chronicles
In the realm of romance, magpies embody monogamy, with pairs maintaining territorial togetherness for a lifetime.
The courtship saga initiates with the female’s pleas for sustenance, leading to the delicate dance of courtship feeding by the male.
Guarding the female during breeding underscores magpies’ commitment, solidifying their reputation as intelligent and easily tamed companions.
Females lay 3-9 eggs, nurturing a sole brood annually through a meticulous incubation period of 16-19 days, followed by 24-30 days of nestling care.
Homing Instinct
Similar to most other pigeons, English Magpie pigeons also have innate homing instincts. While some pigeons of this breed partake in races, generally they are bred for their outlook and not homing ability.
These birds will be able to return home from a short distance, but the same can’t be said for long distances. So, don’t expect much homing capabilities from English Magpie pigeons.
Breeding And Maintenance
In the case of breeding, you have to be careful when it comes to picking a pair and the process like care, nutrition, environment and other factors.

Otherwise, it can harm the pigeon’s reproduction capability. They are fancy birds and require your full attention.
Information about Raising and Breeding
The first for a breeder is to choose a healthy pair. If you want specific traits, then choose a male/female from a specific lineage. Provide them with a spacious nesting box or enclosed nesting area.
It’s breeders’ responsibility to check if they are predator-free. After laying the eggs, the incubation period goes from 17 to 19 days. Pigeon milk (a special secretion) is fed to the squabs by both magpie pigeon parents.
Some Tips and Considerations for Successful Breeding
- Pick the Right Partners: Choose magpies that complement each other. This helps create strong and healthy baby magpies with a variety of good traits.
- Keep a Small Group: Have 5-6 magpies in a group. This makes them less stressed and more likely to have babies naturally without any problems.
- Protect the Moms: Make sure the girl magpies are safe from other boys. This helps them feel secure, and they can focus on taking care of their babies without any problems.
- Fun and Learning: Give magpies things to do and teach them. This keeps them happy and healthy, making it more likely for them to have babies successfully.
- No Monkey Nuts in Baby Season: Be careful with the food you give them during baby season. Using monkey nuts can attract magpies and might harm the nests. Choose safer foods to keep the babies safe.
Follow these simple steps, and you’ll have a higher chance of having lots of healthy and happy baby magpies. Taking care of these details makes sure your magpie family grows strong and stays safe.
Conclusion
English Magpie Pigeon is easily accessible beyond the U.K. and U.S.A. It is a fancy pigeon breed and you need to have access to pigeon fanciers for adoption in cases outside these countries.
These pigeons are better in colder temperatures than in extreme heat. Also, many mix Magpie and Magpie Pigeons as the same; both of these birds are different.
Some pigeon collectors choose illegal ways to import these pigeons. So, always get them from ethical breeders by collecting enough information.
References
- Hashemi and David L. Williams “MEASUREMENT OF INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE IN THE DOMESTIC PIGEON (COLUMBIA LIVIA),” Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine 47(3), 935-938, (1 September 2016). https://doi.org/10.1638/2015-0102.1″
- Sabrina Schalz, Warren D. Horrod-Wilson, Keir Chauhan “The Prevalence of Litter Foraging Among U.K. Birds Lessons Learned From A Citizen Science Project, https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.11.16.468840”
